Robots.txt Is Blocking All Crawling: What It Means, Why It Happens, and How to Fix It
f your website’s robots.txt file is blocking all crawling, search engines are being explicitly told not to access your site at all.
This is one of the most severe technical SEO issues possible. When it happens, pages cannot be crawled, cannot be indexed, and will not appear in search results — regardless of content quality.
This article explains what it means when robots.txt blocks all crawling, why it often happens by mistake, and exactly how to fix it safely.
What is robots.txt?
robots.txt is a plain text file placed at the root of a website that gives instructions to search engine crawlers.
Example location:
https://example.com/robots.txt
It tells crawlers:
- Which areas of the site they may access
- Which areas they must avoid
- Where supporting files like sitemaps are located
Importantly, robots.txt controls crawling, not ranking — but without crawling, ranking is impossible.
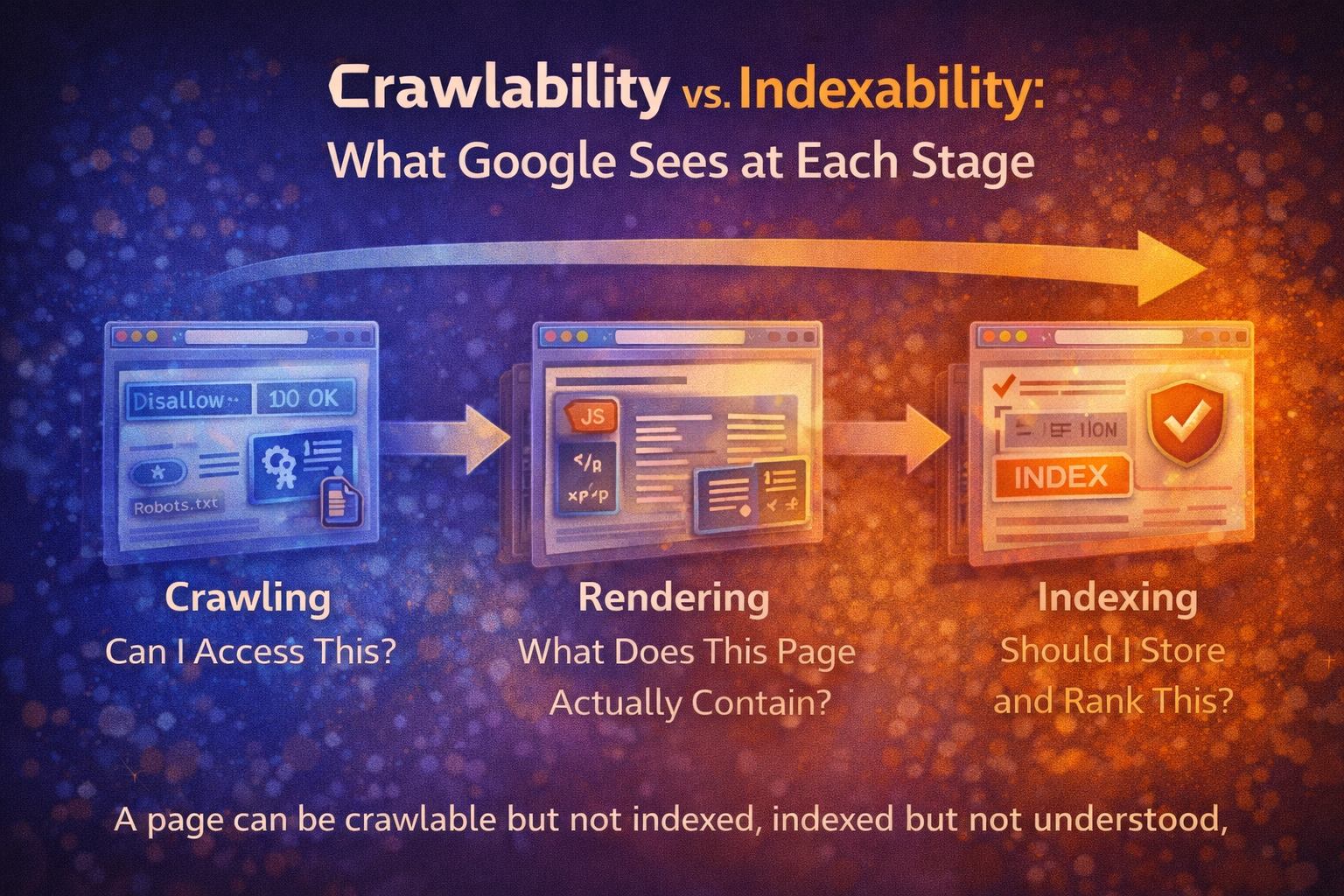
What does “blocking all crawling” mean?
A site is blocking all crawling when its robots.txt file includes rules that disallow every crawler from accessing every path.
The most common example:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
This tells all crawlers to avoid all URLs on the site.
When this rule is present:
- Search engines cannot crawl pages
- Content cannot be indexed
- Existing indexed pages may drop out over time
- SEO visibility collapses
Why this is a critical SEO issue
Blocking all crawling effectively removes your site from search engines.
Key consequences:
- Pages stop appearing in search results
- New content is never discovered
- Updates are ignored
- Internal links are not followed
- Structured data is not processed
From an SEO perspective, the site becomes invisible.
Common reasons robots.txt blocks everything
This issue is almost always accidental.
1. Development or staging leftovers
Developers often block crawlers during development and forget to remove the rule before launch.
2. Misunderstood “privacy” attempts
Some site owners incorrectly believe robots.txt hides content. It does not — it only blocks crawling.
3. CMS or plugin misconfiguration
Certain SEO, security, or maintenance plugins can overwrite robots.txt without warning.
4. Copy-paste errors
A single forward slash (/) in the wrong place can block the entire site.
robots.txt vs indexing: a critical distinction
Blocking crawling is not the same as preventing indexing.
robots.txtblocks accessnoindexcontrols indexing
If a page is blocked by robots.txt, search engines:
- Cannot see its content
- Cannot see meta tags
- Cannot see
noindexdirectives
This often leads to confusing and unintended results.
How search engines treat blocked sites
Search engines such as Google will respect robots.txt rules.
If crawling is blocked:
- Pages may remain indexed temporarily (without content)
- Snippets may disappear
- Rankings decay
- Eventually, pages are removed entirely
This behaviour is expected and correct.
How to confirm robots.txt is blocking everything
Check the file directly in your browser:
/robots.txt
Look for:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
If present, crawling is blocked.
SEO audit tools should treat this as a critical failure, not a warning.
How to fix robots.txt blocking all crawling
Step 1: Decide what should be crawlable
Most public websites should allow crawling of all core pages.
Step 2: Replace the blocking rule
A basic, crawl-friendly configuration:
User-agent: *
Disallow:
This allows all crawlers to access all URLs.
Step 3: Keep intentional exclusions only
If needed, block specific paths instead of everything:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /login/
Be precise. Broad rules cause damage.
Step 4: Retest immediately
Once updated:
- Crawlers can access pages again
- Indexing resumes
- Rankings may gradually recover
robots.txt and sitemaps
A well-configured robots.txt often includes a sitemap reference:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
This helps crawlers discover URLs faster — but only if crawling is allowed.
If crawling is blocked, sitemap links are ignored.
How this issue should appear in an SEO audit
When detected, an audit should clearly state:
- ❌ Crawling is blocked site-wide
- ❌ Pages cannot be indexed
- ❌ SEO visibility is disabled
- ❌ Immediate fix required
There is no safe scenario where blocking all crawling on a public website is acceptable.
Edge cases where blocking all crawling is intentional
Very rare, but possible:
- Private internal tools
- Temporary maintenance environments
- Auth-only applications
- Closed beta platforms
If the site is meant to be public, blocking all crawling is always a mistake.
Final thought
A single line in robots.txt can override every other SEO effort you make.
Perfect content, fast performance, clean structure — none of it matters if crawlers are told to stay out.
If your audit reports that robots.txt is blocking all crawling, this is not an optimisation task.
It is an emergency fix.


Post Comment